Best Crypto ICOs - New Upcoming ICO Calendar for 2024
Welcome to ICOBench.com. Use our ICO calendar to keep track of upcoming and active ICOs, delving into what makes each project unique. Our mission is to high-potential new ICOs before they hit the mainstream by offering reviews, ratings, and a comprehensive ICO calendar to stay up-to-date on crucial dates and developments.

Dogeverse
Dogeverse is the first true multi-chain Meme Coin. Alongside Cosmo, the Doge, it will bring the $DOGEVERSE to all major blockchains.
Amount raised: $300k+
Chain: Multi-Chain
Feature: Meme Coin

Slothana
Slothana is looking to replicate the success of recent Solana ICOs like SLERF & BOME and raised over $500k within hours of launching.
Amount Raised: $500k+
Chain: SOL
Feature: Solana Meme Coin
MegaDice
Positioned among the leading brands in the realm of crypto casinos, MegaDice’s primary aim revolves around expansion and enhancing the experience for its players with the introduction of $DICE.
Amount Raised: $300k+
Chain: SOL
Feature: GambleFi Token

99Bitcoins
99Bitcoins is an innovative crypto project from the same Youtube channel with more than 700k subscribers.
It is designed to reward users for learning about cryptocurrency.
Amount Raised: $300k
Chain: ETH
Feature: Learn-to-Earn
5thScape
5th Scape is an innovative project that combines crypto with VR gaming. Holders cget lifetime access to VR content and in-game advantages, as well as other perks.
Amount raised: 1.5M
Chain: ETH
Feature: VR Gaming

Sponge V2
Sponge V2 is an upgraded version of the Sponge meme coin that saw 100x gains in 2023. You can earn Sponge V2 tokens by staking Sponge.
Chain: ETH
Feature: Staking & P2E Games
ICO Calendar
Top ICOs & Upcoming ICO Calendar| ICO NAME | CURRENT STAGE | PLATFORM | START DATE | END DATE | ROI [USD] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Dogeverse Dogeverse |
PRESALE STAGE 1 Ends in 10 days |
 Multi-Chain Multi-Chain |
Apr 08, 2024 | May 06, 2024 | - | First Multi-Chain Meme Coin |
 Slothana Slothana |
AIRDROP Ends in 23 days |
Apr 01, 2024 | May 19, 2024 | - | Limited Presale Airdrop | |
 99Bitcoins 99Bitcoins |
PRESALE STAGE 1 Ends in 15 days |
Apr 10, 2024 | May 11, 2024 | - | Established Media Platform Coin with Huge Community | |
| PRESALE STAGE 1 Ends in 21 days |
Apr 17, 2024 | May 17, 2024 | - | Fast-Selling GambleFi Presale | ||
 5th Scape 5th Scape |
PRESALE STAGE 1 Ended 25 days ago |
Jan 08, 2024 | Mar 31, 2024 | - | Combining Crypto with VR | |
 Slothana Slothana |
ICO Ends in 4 days |
 solana solana |
Mar 26, 2024 | Apr 29, 2024 | - | |
 Dogeverse Dogeverse |
Pre-Sale: Stage 3 Ends in 5 days |
 ETH, SOL, MATIC, AVAX, Base Chain, Binance Smart Chain ETH, SOL, MATIC, AVAX, Base Chain, Binance Smart Chain |
Apr 23, 2024 | Apr 30, 2024 | - | |
 Hypeloot Hypeloot |
ICO Ends in 5 days |
 ethereum ethereum |
Feb 01, 2024 | Apr 30, 2024 | - | |
 99 Bitcoins 99 Bitcoins |
Pre-Sale Ends in 36 days |
Apr 10, 2024 | May 31, 2024 | - | ||
 Fortified X Fortified X |
Private Pre-Sale Ends in 5 days |
 Binance Smart Chain Binance Smart Chain |
Apr 01, 2024 | Apr 30, 2024 | - | |
 Healix Healix |
Private Pre-Sale Ends in 35 days |
 Binance Smart Chain Binance Smart Chain |
Mar 18, 2024 | May 30, 2024 | - | |
 SpongeBob V2 SpongeBob V2 |
ICO Ends in 158 days |
 ethereum ethereum |
Dec 18, 2023 | Sep 30, 2024 | - | |
 ALEIT ALEIT |
Pre-Sale Ends in 0 days |
 Binance Smart Chain Binance Smart Chain |
Mar 25, 2024 | Apr 25, 2024 | - | |
 BlowFish Tequila BlowFish Tequila |
Private Pre-Sale Ends in 1 days |
 ethereum ethereum |
Mar 26, 2024 | Apr 26, 2024 | - | |
 Blastup Blastup |
Pre-Sale: Stage 7 Ends in 1 days |
 blast-io blast-io |
Apr 12, 2024 | Apr 26, 2024 | - | |
 Bitbot Bitbot |
Pre-Sale: Stage 9 Ends in 3 days |
ETH, SOL | Apr 19, 2024 | Apr 28, 2024 | - | |
 Aurum AI Aurum AI |
Pre-Sale: Phase 1 Ends in 5 days |
 Binance Smart Chain Binance Smart Chain |
Apr 01, 2024 | Apr 30, 2024 | - | |
 Brics Coin Brics Coin |
Pre-Sale: Round 2 Ends in 5 days |
 tron tron |
Feb 01, 2024 | Apr 30, 2024 | - | |
 CloudBTC CloudBTC |
Pre-Sale: Stage 6 Ends in 5 days |
 ethereum ethereum |
Jan 01, 1970 | Apr 30, 2024 | - |
Testimonials from Crypto Investors
What are the Best Crypto ICOs?
Here are five of the most interesting crypto ICOs currently running.
- Dogeverse — The ‘chain hopping’ Doge coin that will launch on 6 blockchain networks.
- Slothana — The presale of a meme coin built on Solana has garnered $500k in funding.
- 99Bitcoins — Top-notch ICO project for learn-to-earn with affordable presale prices.
- MegaDice (DICE) —The newest GambleFi ICO project with a fast-selling presale.
- 5th Scape — New metaverse token presale offering VR hardware and VR games.
- Sponge V2 — Best crypto ICO to buy now after Sponge V1 returned 100x to early investors.
- Smog — The top crypto presale offers substantial airdrop rewards along with a staking yield of 42%.
- eTukTuk — Leading ICO project that aims to fight climate change with sustainable transportation.
- Bitcoin Minetrix — Top new crypto presale project aiming to make Bitcoin mining affordable.
- Dogecoin20 — The eco-friendly variant of DOGE providing enticing staking rewards for its initial backers.
1. Dogeverse – The first multi-chain Doge token that will launch on 6 networks
Doge-themed tokens have a history of rewarding investors generously. However, these meme coins have always been limited by their underlying technology.
Dogeverse is a new meme token that offers a solution – a ‘chain hopping’ meme coin that will be available on 6 major blockchain networks.

Cosmo the dog is the symbol of the new meme project. Using his multi-chain abilities, he will seamlessly hop from chain-to-chain, connecting the meme community and offering excellent utility.
The DOGEVERSE token stands out from other meme coins due to its impressive utility. The token can be used for on-chain staking which will encourage long-term participation and investor demand. Furthermore, DOGEVERSE can be used across different blockchain networks which will improve access to the Doge community.
DOGEVERSE has a limited supply of 200 billion. 15% of these tokens are available to buy during presale and the remaining coins will be used for marketing, staking, exchange listings, liquidity and project development.
The token will start its journey as a typical meme coin. However, the official project website hints at investor rewards which could generate returns for early investors and bring added utility to the token. You can buy DOGEVERSE at presale using ETH, BNB or MATIC.
Your money is at risk.
2. Slothana — The Presale Of A Meme Coin Built On Solana Has Garnered $500k In Funding
If you are looking to take advantage of the potential of explosive growth in 2024, Slothana may be worth considering. This SOL-based meme token has generated over $500k in a short period after the release and is one of many meme tokens that are ready to reach new heights.

Moreover, presale investors will surely gain from the following airdrop event set to happen. To obtain the said tokens, simply connect your Solana wallet to the presale platform and exchange SOL for them.
However, users should also understand that Slothana has little utility to it other than the ability to generate substantial profits. In other words, it is an inherently high-risk short-term investment.
Your money is at risk.
3. MegaDice – The Latest GambleFi ICO Project With Massive Potential
The DICE token serves as the primary cryptocurrency within the renowned MegaDice platform, a stalwart in the cryptocurrency casino industry. DICE enables gameplay, unlocks exclusive perks, grants access to bonuses, and facilitates participation in crypto airdrops.

A portion of MegaDice’s revenue, comprising transaction fees and profits, is distributed among DICE token holders. This revenue-sharing model incentivizes the ownership of DICE tokens and active engagement within the MegaDice ecosystem.
With its solid reputation in the crypto casino sector, MegaDice is poised to attract significant demand for its token.
Don’t miss the chance to purchase DICE at a discounted rate during the ongoing presale event.
Your money is at risk.
4. 99Bitcoins – Top-notch ICO Project For Learn-to-earn With Affordable Presale Prices
99Bitcoins is one of the most trending cryptocurrencies on the market right now. Unlike many projects focusing solely on speculative value, 99Bitcoins implements a one-of-a-kind Learn-to-learning model.
99Bitcoins’ L2E approach transforms cryptocurrency learning into an engaging and beneficial experience. Users can earn rewards in the form of $99BTC tokens by completing educational courses and quizzes on the platform. This pioneering initiative incentivizes people to dive into cryptocurrencies while earning passive income.

With the increasing adoption of cryptocurrencies, especially in a bull market like 2024, a significant increase in demand for cryptocurrency education is anticipated. 99Bitcoins, one of the first projects to implement the L2E model in the crypto space, is well positioned to capitalize on this trend.
The $99BTC presale offers an exciting opportunity for early investors to participate in a project with a novel and attractive approach. The token price is expected to reach $0.00113 by the end of the presale, which comprises 14 stages. The project has a hard cap target of over $11 million.
Your money is at risk.
5. 5th Scape — Hot New Presale Focused on the Metaverse Through VR Hardware and VR Games
5th Scape is a new token presale aiming to redefine the concept of metaverse by using their own VR hardware, such as a headset and a chair, and their own VR games. Native to the project is the 5SCAPE token, which will be used as a currency within the ecosystem, as well as to give holders special features, exclusive access and in-game assets.
Buy the 5SCAPE token on the token presale site by using a MetaMask wallet, or any other Ethereum wallet. Use ETH, MATIC, BNB, USDT or a card to complete the purchase.
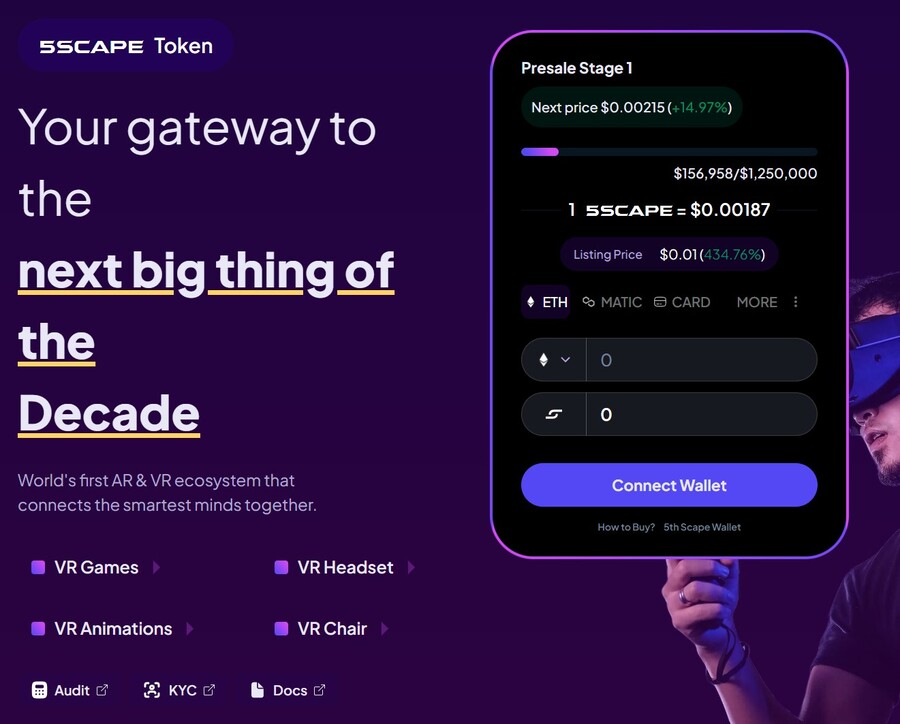
The goal of the presale is to raise $15 million to help the project development. There will be 5.211 billion tokens with the presale getting 80% of it (4.164 billion). Of those, 40% will be unlocked at the token generation event, while the remaining tokens will have 8 week lock and 8-month vesting period, per the 5th Scape whitepaper.
make sure to follow 5th Scape on X and join the 5th Scape Telegram channel to get the latest information.
Your money is at risk.
6. Sponge V2 — New Crypto Presale With Over $3 Million Raised so Far
Sponge V2 is a popular meme coin presale that has already raised over $3 million. Its previous version, Sponge V1, peaked at a $100 million market cap in 2023, returning over 100x to early investors. Sponge V2 aims to outperform its predecessor by adding a play-to-earn racing game with meme characters, which is expected to drop in sometime in 2024. This will bring utility to the Sponge V2 token and potentially increase the token demand.
The only way to get Sponge V2 tokens is to buy them in a presale where you connect your Ethereum wallet to the presale site and use ETH or USDT to make the purchase. Just make sure to leave some ETH in your wallet to pay for the transaction fees. While you wait, you can stake your tokens to earn 235% APY.
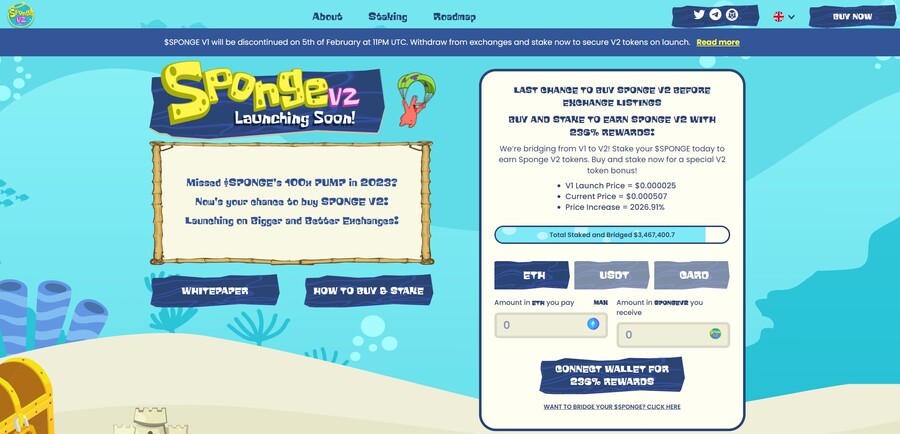
Follow Sponge V2 on X and join Sponge V2 Telegram channel to stay up to date with the latest news. Read the Sponge V2 whitepaper to learn more about the project.
Your money is at risk.
7. Smog — The Top Crypto Presale Offers Substantial Airdrop Rewards Along With A Staking Yield Of 42%
A new meme coin, Smog ($SMOG), was launched on Jupiter DEX on the Solana network on February 7, 2024. The coin shares its appearance with previous successful launches, such as Bonk, Myro, or Dogwifhat, and promises to capitalize their success. Initially traded at $0.001419, $SMOG went up 2000% in the course of a week to $0.04. The project is built around the concept of the ‘Greatest SOL Airdrop’, a unique mechanism for incentivizing active community and on-chain involvement.
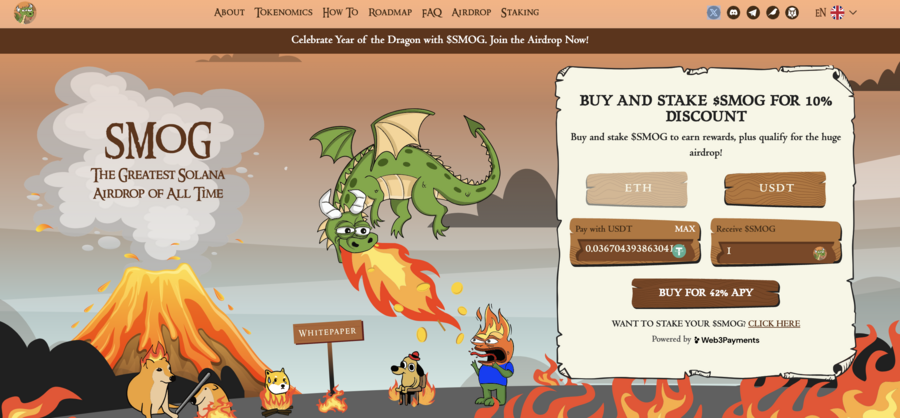
The lack of a presale behind Smog means that there are no initial holders that enjoy preferential treatment, which significantly adds to the coin’s credibility. Out of the proposed total supply of 1.4 billion, Smog has allocated 50% to marketing and 35% – to the airdrop to ensure a wide reach.
Another attractive component of the offer is the 42% APY yield from the staking promotion, which has a 90-day lock-in and, therefore, promotes long-term engagement. By creating an Ethereum bridge for the sake of cross-chain interoperability, Smog opens up potential millions of users to its offer. A further 10% of the total coins will go into the centralized exchange launch and 5% into decentralized exchange liquidity.
Your money is at risk.
8. eTukTuk — New Crypto Presale Aiming to Bring Energy-Efficient Solutions to Transportation
eTukTuk is one of the rare crypto projects that aim to solve real-world issues, such as climate change. The way it plans to do it is by introducing electric Tuktuk vehicles and electric charging stations. The project’s native token is TUK, which will be used as a means of exchange within the ecosystem.
To participate in the token presale, you need to visit the presale site and connect your Ethereum-based wallet. Use either BNB, ETH, USDT or card. Once you have your tokens, you can stake them to earn 295% APY. The team recommends buying the token on the BNB Smart Chain, which is where you will stake your tokens.
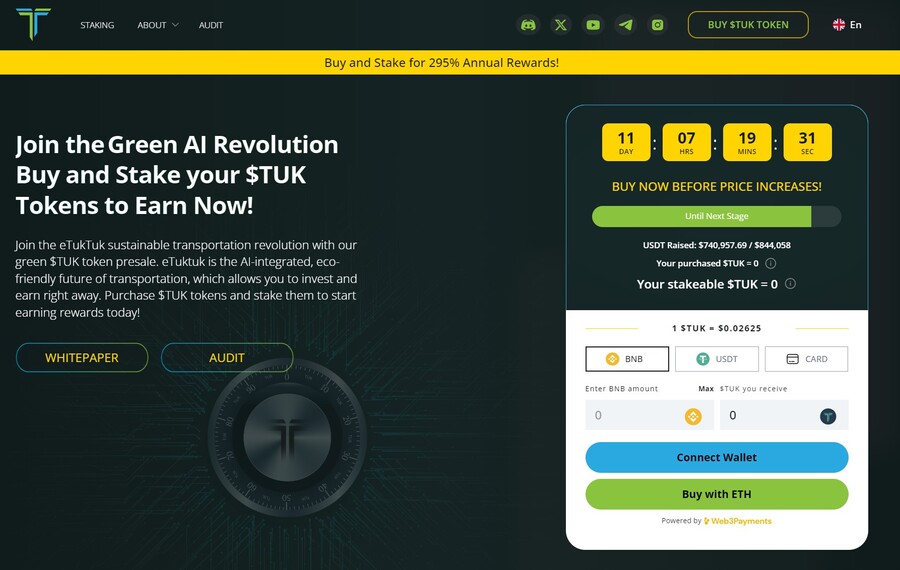
There will be 2 billion TUK tokens, but only 6% of those will be used in the presale, according to the eTukTuk whitepaper. You can still stake your tokens even while waiting for the presale to end and increase the number of tokens you hold. That’s because the staking APY stands at 118% at the moment of writing.
Follow eTukTuk on X and join the eTukTuk Telegram channel to get the latest information about the presale and the project.
Your money is at risk.
9. Bitcoin Minetrix — Stake-to-Mine Bitcoin With This New Token Presale
Bitcoin Minetrix is a hot new presale that aims to build a stake-to-mine model where you can stake your BTCMTX tokens to earn Bitcoin mining credits. You can convert these credits for actual Bitcoin without needing expensive mining hardware or large amounts of electricity. Because of that, the Bitcoin Minetrix ICO has raised over $10 million so far.
Purchase BTCMTX tokens on the Bitcoin Minetrix presale site by connecting your Ethereum wallet. Use ETH, USDT or a card to make the purchase. There’s also the option to buy with MATIC and BNB, but these two coins aren’t eligible for the staking reward, which stands at 66% APY as of this writing.

There are 4 billion tokens in total, with 2.8 billion of them dedicated for the token presale, according to the Bitcoin Minetrix whitepaper. There will be multiple presale rounds and with each round, the token price will increase.
Stay up to date by following Bitcoin Minetrix on X and join the Bitcoin Minetrix Telegram channel.
Your money is at risk.
10. Dogecoin20 — The Eco-friendly Variant Of Doge Providing Enticing Staking Rewards For Its Initial Backers.
Dogecoin20, a new meme token, is a radical reimagining of its precursor, Dogecoin. This is the first iteration to address limitations and promote sustainability. Dogecoin20 was created in 2013 as an intellectual model for Dogecoin concocted by Elon Musk.
It merges meme culture and progressive tokenomics into a single, simple-to-understand token via a deflationary model and on-chain staking. This endeavor appeals to meme addicts and savvy investors who want their meme and money too.

In addition, Dogecoin20 has a sustainable staking system with an APY of more than 200%, offering early adopters with passively huge returns proportional to stake size over time. The project involves a series of presales and other Uniswap listings, as well as various actions to help causes committed to charitable initiatives and community projects. Dogecoin20 may produce upward price pressure using a fixed token inventory and sustainable stacking. It strives to become a sustainable and philanthropic meme token.
Your money is at risk.
What is an ICO?
First things first: What is an ICO? An ICO, or “Initial Coin Offering,” is a fundraising mechanism similar to crowdfunding, used mainly by cryptocurrency startups. These are also often called crypto presales. Projects use new ICOs to raise capital by offering investors the chance to purchase their native tokens using established cryptocurrencies, like Ethereum (ETH) or Tether (USDT).
By purchasing these tokens, investors gain a sort of “share” in the project. However, unlike traditional shares, these tokens can also play a functional role in the project’s ecosystem. For example, they may act as a transactional currency or grant access to specific features, like governance voting rights.
The main draw for investors lies in the hope that the value of these altcoins will increase significantly once the underlying project becomes fully developed and operational. In turn, this could offer substantial returns to these investors.
Many active ICO Drops allow investors to purchase tokens at a discounted rate before they’re listed on centralized or decentralized exchanges. This early-bird advantage enables investors to position themselves strategically for outsized gains – if the token’s value rises upon listing.
However, as with all investments, thorough research and a deep understanding of a project’s fundamentals are essential before venturing into ICOs, especially considering the volatile nature of the cryptocurrency market.
How Do ICOs Work?
The ICO process tends to unfold over several stages, often beginning with what’s known as the ‘Pre-ICO’ stage. During this stage, the project is officially announced, a whitepaper is released, and marketing activities create a buzz – usually on social media channels like Twitter and Instagram.
Following this, the official token sale commences. This phase invites early investors to purchase the project’s native token using established cryptocurrencies which can be acquired from a leading broker or exchange. During the token sale, a hard cap, token price, and list of accepted coins are explicitly noted.
Once the token sale ends, which usually occurs when the hard cap has been hit, or the developers choose to conclude it early, ‘Post-ICO’ activities take place. This usually involves allowing early investors to claim their purchased tokens before launching the token on centralized or decentralized exchanges (or both).
As seen from the ICO process, this setup is similar to crowdfunding, requiring intense effort from the project’s developers and engagement from the investment community.
Keep Up-to-Date with our ICO Calendar
Navigating the dynamic world of active ICOs can be daunting, especially given the number of new projects entering the market each week. Due to this, we at ICOBench have curated a comprehensive ICO calendar designed for both market newcomers and veteran investors.
This calendar provides a comprehensive upcoming ICOs and active projects, ensuring readers never miss potential investment opportunities. Beyond just dates, our ICO calendar offers crucial details about each project, helping investors quickly gauge the relevance and potential of every listed project. The ICO projects listed range from meme coins, AI crypto coins, shitcoins and cryptocurrencies which can explode, thus offering investors a wide-range of investment opportunities.
Reviewing Upcoming and Active ICOs
It’s crucial to distinguish genuine ICOs from less reliable ones. At ICOBench, our approach to reviewing and ranking upcoming ICOs is rigorous and transparent. We usually begin with a comprehensive analysis of the project’s whitepaper, which contains information on its mission, underlying technology, and the problem(s) the developers seek to address.
However, the whitepaper is just the starting point – it’s also important to take a close look at an ICO project’s development team. While experienced team members can indicate potential success, inexperienced ones might raise red flags.
We also consider the tokenomics of upcoming ICOs. Tokenomics refers to the structure and strategy of a token’s distribution, including how many tokens there are, what percentage is allocated to the development team, and whether there is a burn mechanism in place.
Another crucial aspect of our review process is evaluating a project’s community engagement. An active and engaged community often indicates genuine interest and support. However, it’s also crucial to note how the developers interact with the community; for example, if they are responsive and happy to address investor concerns.
Incorporating these factors is pivotal to our review and ranking process at ICOBench. It’s not just about identifying ICOs with promising returns potential but also about ensuring our readers are informed about projects with solid foundations.
Unfortunately, ICO scams are not uncommon, so differentiating between a credible ICO and a fraudulent one is often down to in-depth research. Our systematic approach aims to help our readers with this research – fostering a safer and more informed investment environment for everyone.
Are ICOs Legal?
The legal standing of ICOs varies across jurisdictions and can be complex. In some countries, ICOs operate within a clear regulatory framework; however, in others, they may fall into “gray areas.”
For example, in some areas of the US, ICOs must adhere to strict regulations. In contrast, other nations, like Switzerland, may have a more laid-back approach where ICO projects don’t need to obtain a license or register with the authorities.
Some countries have even prohibited ICOs outright. A prime example is China, which banned all forms of ICOs in 2017, citing fraud and market instability concerns.
The legal environment surrounding ICOs is so complex because projects must meet particular requirements, like registering with regulatory bodies, adhering to anti-money laundering laws, and providing disclosures. Investors must also be mindful of these laws to ensure they participate in ICOs properly.
Overall, the legality of ICOs is not universally consistent, given the continuous changes in crypto regulation and the different laws depending on the specific region. As such, investors must conduct thorough due diligence and comply with all applicable rules before participating in an ICO.
How to Safely Invest in an ICO
Investing in upcoming ICOs offers the opportunity to enter early into promising projects – but it also entails risks. Ensuring a safe investment requires careful consideration of several factors:
KYC Compliance
KYC procedures are implemented by some ICO projects to comply with anti-money laundering regulations. These procedures require investors to provide identification and prove they are who they say they are. As such, investing in ICOs that follow KYC protocols can add an extra layer of security.
Smart Contract Audit
Smart contracts are what underpin the mechanics of any token sale. A third-party audit of the smart contract ensures it’s free of vulnerabilities and malicious code. Investing in ICOs without a smart contract audit can expose investors to risks, including the potential loss of capital.
Tokenomics
Understanding a project’s tokenomics is vital. This includes reviewing the total token supply, distribution strategy, and how the tokens will be used. Poor tokenomics may lead to oversupply issues or other imbalances, ultimately affecting price.
Project Whitepaper
A project’s whitepaper provides insights into the development team’s vision, the project’s technology, and the future roadmap. Analyzing this whitepaper helps determine a project’s viability and potential for success.
Development Team
The experience, credibility, and transparency of the development team can be indicative of a project’s potential. A team with a proven track record, clear roles, and active community engagement is often a positive sign.
Legal Compliance
Finally, understanding the legal environment and ensuring that the ICO complies with local regulations is crucial since it safeguards against potential legal implications or fraud.
All in all, safely investing in active ICOs requires a comprehensive approach, considering all of the factors laid out above. This allows investors to minimize risk and identify genuine opportunities in the rapidly-evolving ICO space.
To help you out, we carry out a comprehensive review of every project on our ICO to list to ensure they’re legit.
What Returns Can I Make Investing in ICOs?
Investing in new ICOs can be a double-edged sword, given that they can yield staggering profits or substantial losses. The return on investment (ROI) in ICOs is often unpredictable and influenced by countless factors. These include:
Market dynamics, like the overall sentiment in the crypto market.
- Project fundamentals, such as the development team’s experience, the project’s roadmap, and the level of community engagement.
- The timing of investment
- The specific investment strategy (e.g., one-off investment, staggered investing, etc.)
While some ICOs have generated 10x, 100x, or even 1,000x returns for early investors, others have failed miserably, resulting in investors losing their initial capital. As such, conducting due diligence on the project, the developers, and the viability of the token’s use case is crucial.
However, a prime example of a highly-successful ICO is that of Ethereum (ETH). Ethereum raised over $17 million during its ICO in 2014, selling ETH tokens for around $0.30 each. Today, ETH trades at over $1,600 per token, meaning that early investors have seen returns of over 5,300x their initial investment. NEO is another famous example that saw the token’s price from $180 compared to its ICO price of $0.03.
There are also many recent examples of ICOs that have proved to be successful investments. These include:
- Sui, which raised over $50 million in its ICO, was sold for $0.1 in the presale round and shot up to $1.5 after listing. Its currently trading at $0.5, which is still 5x higher than its ICO price.
- Sei, one of the most recent examples, sold for $0.015 in its ICO and exploded over 3,000% and hit $0.26, partly helped by it being listed on Binance.
- BTC20, a stake-to-earn coin inspired by Bitcoin, recently rose by 600% following its IEO.
Ultimately, the return on investing in ICOs is speculative and uncertain. Diligent research, smart risk management, and an understanding of the project and broader market dynamics are essential. Investors must always consider their risk tolerance and investment goals when venturing into the ICO space.
How Often Do New Crypto ICOs Take Place?
New ICOs launch on a weekly basis, with some running for relatively short periods and others for longer ones. So, there are certainly no shortage of ICOs to pick from, but the challenge is finding legit projects with genuine potential.
This is why it’s important to read up on a project’s whitepaper and team, engage with the community, and ensure the tokenomics are sound. Of course, you can also use our list of vetted new crypto ICOs as a starting place to find exciting projects.
FAQs
What are ICOs in crypto?
What is the best crypto ICO?
How do I invest in an upcoming ICO?
Where do I find upcoming ICOs?
Are ICOs safe to invest in?
Can you make money investing in ICOs?
What is the next ICO?
 Crypto Presales
Crypto Presales
The Best Crypto Presales to Discover Emerging ICOs & Cryptocurrencies
Icobench.com investigates current and upcoming Initial Coin Offerings, which CryptoPresales offer as a curated and always up-to-date cryptocurrency list of trending and upcoming ICOs.
Read on to explore the best crypto presales and best ICOs of 2024.




 Crypto Presales
Crypto Presales